The Ransomware Epidemic: How SMBs Are Being Impacted and What You Can Do to Defend Your Business
Ransomware has emerged as a formidable threat to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), often leading to significant financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Unlike larger corporations with extensive cybersecurity infrastructures, SMBs frequently lack the resources to effectively combat such sophisticated cyber threats, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
The Impact of Ransomware on SMBsM
The consequences of ransomware attacks on SMBs are profound. Financially, the costs can be staggering, encompassing ransom payments, data recovery expenses, and potential regulatory fines. Operationally, businesses may face prolonged downtimes, losing productivity and customer trust. In severe cases, the damage inflicted by ransomware can be so extensive that some SMBs are unable to recover, leading to permanent closure.
Top Small Business Cyber Security Statistics 2024
- Accenture’s Cybercrime study reveals nearly 43% of cyber-attacks on small businesses.
- 55% of ransomware hit businesses with fewer than 100 employees, while another 75% of attacks targeted companies making less than $50 million in revenue.
- Only 14% of these accounted SMBs are prepared to face such an attack.
- On average, SMBs spend between $826 and $653,587 on cybersecurity incidents.
- 95% of cybersecurity breaches are attributed to human error. (World Economic Forum)
Ransomware-as-a-Service Has Increased Cybercrime Dramatically
We thought it would be helpful to share some of the most well-known ransomware attacks on small businesses to inform you how many occur and how sophisticated they have become in the past three years or so. What is obvious to those in the industry is that Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has changed the cybersecurity environment dramatically.
RaaS kits are widely available on the dark web, with prices ranging from as low as $40 per month to several thousand dollars, depending on the sophistication of the malware and the services included.
The accessibility and affordability of these kits have led to a surge in ransomware attacks, mainly targeting small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Last year alone, RaaS operations accounted for the majority of ransomware incidents reported globally. And according to SonicWall, over 493.3 million ransomware attacks were detected.
Case Studies of Ransomware Attacks on SMBs
- Akira Ransomware Attack (2023)
As of April 2024, the Akira ransomware group had impacted over 250 organizations and amassed approximately $42 million in ransom payments. By November 2024, the group had expanded its reach, affecting more than 350 organizations globally.In early 2023, the Akira ransomware group targeted several SMBs across various industries. The malware encrypted files, appending the “.akira” extension, and demanded Bitcoin payments for decryption keys. Employing a double extortion tactic, Akira not only encrypted data but also threatened to leak sensitive information if the ransom was not paid. Many affected businesses faced the dilemma of paying the ransom or risking data exposure, leading to significant financial and reputational repercussions.
- Dharma Ransomware Incidents
Operating since 2016, Dharma ransomware has been distributed under a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model, allowing affiliates to launch attacks against various targets, including SMBs. Dharma affiliates do not appear to discriminate among industries, making SMBs particularly vulnerable. The malware encrypts files and demands ransom payments, often leaving businesses with the difficult choice of paying the ransom or attempting data recovery through other means.
- NetWalker Ransomware Attacks
NetWalker ransomware, written in C++, has been advertised as a RaaS on forums by a user known to be part of a group designated as CIRCUS SPIDER. NetWalker encrypts files on the local system, maps network shares, and enumerates the network for additional shares, attempting to access them using the security tokens from all logged-in users on the victim’s system. This method allows the ransomware to spread rapidly within an organization’s network, causing widespread data encryption and operational disruption.
Cybersecurity risks are on the rise for business leaders, with 68% feeling confident that their risks are increasing (Accenture). 54% of businesses admit that their IT departments lack the experience to manage complex cyberattacks. (Sophos)
Cybersecurity Best Practices to Defend Against Ransomware
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is critical for SMBs to defend against ransomware attacks. The following best practices can significantly reduce the risk:
- Regular Data Backups
- Implementation: Conduct frequent backups of critical data and store them in secure, offline locations. Ensure that backups are tested regularly to confirm their integrity and effectiveness.
- Defense Mechanism: Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to deploy ransomware. Keeping systems updated closes these security gaps, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Keep Software and Systems Updated
- Implementation: Regularly update all software, operating systems, and applications to their latest versions. Enable automatic updates where possible to ensure timely patching of vulnerabilities.
- Defense Mechanism: Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to deploy ransomware. Keeping systems updated closes these security gaps, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Implement Strong Access Controls
- Implementation: Enforce the principle of least privilege by granting users only the access necessary for their roles. Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Defense Mechanism: Restricting user access limits the potential pathways for ransomware to infiltrate and spread within the network. MFA adds an additional verification step, making unauthorized access more challenging for attackers.
- Employee Training and Awareness
- Implementation: Conduct regular cybersecurity training sessions to educate employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe online practices.
- Defense Mechanism: Human error is a common entry point for ransomware. Educated employees are more likely to recognize and avoid malicious links, emails, and attachments, thereby reducing the risk of accidental malware introduction.
- Deploy Advanced Security Solutions
- Implementation: Utilize reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Consider endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions for enhanced protection.
- Defense Mechanism: These tools can detect and block ransomware before it executes, monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, and provide real-time alerts, enabling swift response to potential threats.
- Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
- Implementation: Create a comprehensive incident response plan outlining the steps to take in the event of a ransomware attack. Regularly test and update the plan to ensure its effectiveness.
- Defense Mechanism: A well-prepared response plan enables businesses to act quickly to contain and mitigate the impact of an attack, reducing downtime and facilitating a more efficient recovery process.
- Restrict Macro Execution in Office Files
- Implementation: Configure Office applications to disable macros by default and only enable them for trusted documents.
- Defense Mechanism: Ransomware often uses malicious macros embedded in Office documents to execute. Restricting macro execution prevents this common attack vector.
- Secure Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Access
- Implementation: Disable RDP if not in use. If necessary, restrict access through VPNs, enforce strong passwords, and enable account lockout policies.
- Defense Mechanism: RDP is a frequent target for ransomware attacks. Securing or disabling it reduces the risk of unauthorized remote access.
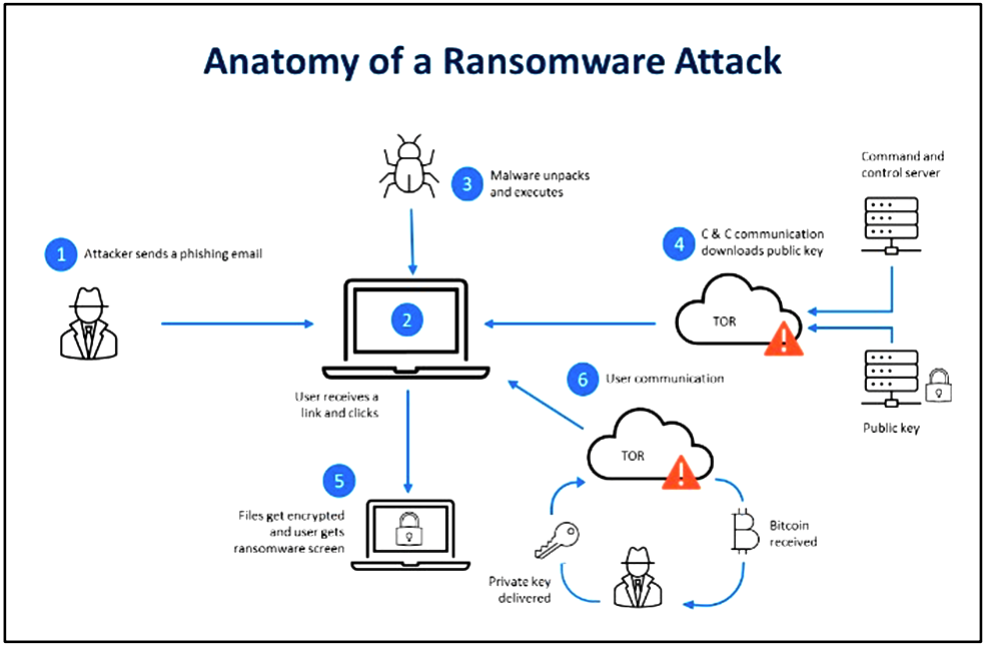
As the case studies demonstrate, ransomware is typically delivered through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links, drive-by downloads from compromised websites, or the exploitation of unpatched software vulnerabilities.Once executed, the ransomware deploys a payload that initiates a series of malicious actions. These include establishing persistence on the target system, escalating privileges, and conducting network reconnaissance to locate valuable data. The ransomware then encrypts files using robust cryptographic algorithms, often targeting backups and shared network drives to maximize impact.
Conclusion
Ransomware continues to devastate small and medium-sized businesses, exploiting limited resources and inadequate defenses. These attacks are not just costly; they threaten the survival of businesses, eroding customer trust and disrupting operations. The stories of Akira, Dharma, and NetWalker highlight the stakes: preparedness is no longer optional.
Adopting robust cybersecurity measures—like regular backups, employee training, and advanced threat detection—your business can transform from a vulnerable target to a fortified operation. Prevention is the most cost-effective strategy, and proactive planning is your best defense.
Now, let’s show you how you can take the first and most important step to protecting your organization against Ransomware.
Falcon Guard’s Innovative Ransomware Preparedness Assessment
Service Overview:
FalconGuard’s Ransomware Preparedness Assessment evaluates your organization’s readiness to prevent, detect, and respond to ransomware threats using industry best practices and cybersecurity expertise.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Analysis of processes, endpoint and email security, network defenses, and data protection.
- Expert Analysis: Insights from seasoned cybersecurity professionals.
- Actionable Insights: Reports with tailored recommendations and prioritized action plans.
- Peace of Mind: Clear understanding of vulnerabilities and steps to mitigate them.
Three-Step Process:
- Pre-Assessment: Information gathering and scheduling.
- Remote Session: Detailed assessment of security domains and collaborative discussions.
- Reporting: Delivery of a comprehensive report with findings, scores, and recommendations.
Business Benefits:
- Enhanced security posture and minimized risks.
- Regulatory compliance and due diligence.
- Business continuity and customer trust protection.
Why FalconGuard?
- Proven cybersecurity expertise.
- Custom-tailored solutions.
- A client-first approach ensuring optimal outcomes.
To learn more about how Falcon Guard can assist with deciding on optimal cybersecurity solutions for your organization, or if you suspect that you have been targeted by an attack, contact us at (858) 349-2610 or fill out our Contact Us form on our website.

